Automating Road Safety Predictions
March 24, 2022
Thanks to financial support from the UK Aid through the World Bank’s Global Road Safety Facility (GRSF), an automated road safety scan system has been developed. This Integrated Framework for Road Safety detects road characteristics from street-level images and provides a road safety prediction for each segment analyzed.

Ideas in action
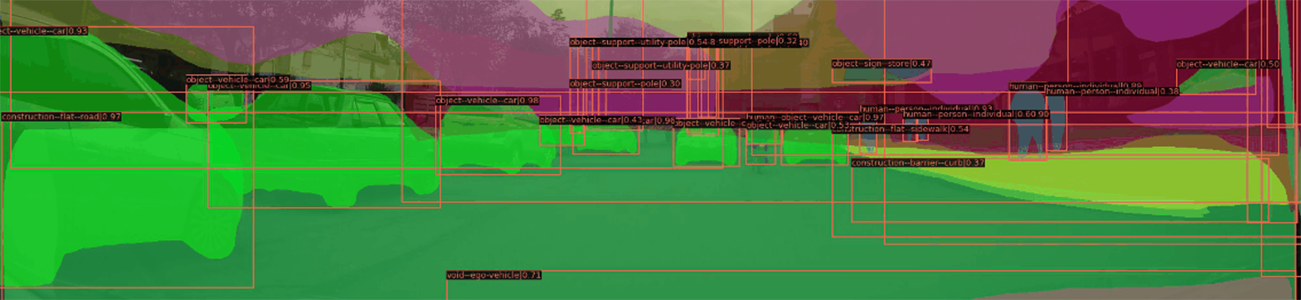
Road segment images can be accessed through an open-source platform, such as Mapillary, or taken on location. The framework can automatically identify 106 street characteristics (based on the Mapillary Vistas dataset), such as road signs, streetlights, street markings, bike lanes, sidewalks, and potholes, thereby reducing reliance on traditional methods of manual image annotations.
The machine learning-based framework was developed by the World Bank's Land and Urban team in East Asia Pacific Region in cooperation with GFDRR’s Global Program for Resilient Housing. Case studies were conducted in Bogotá, Colombia, and Padang, Indonesia. Road segment risk was predicted with 72.5 percent accuracy in Bogotá. While additional data is needed to confirm the framework’s performance in Padang, the workflow is replicable in other locations.
Additional resources
 The full code for the Integrated Framework for Road Safety is freely available for repurposing to a local context.
The full code for the Integrated Framework for Road Safety is freely available for repurposing to a local context.
The framework accompanies a guidance note, Detecting Urban Clues for Road Safety: Leveraging Big Data and Machine Learning, which reviews data requirements for road safety assessments, summarizes relevant big data sources, and offers a practical introduction to using big data and machine learning in road safety evaluations.
Task team
Sarah Elizabeth Antos, Luis Triveno, Jessica Gosling-Goldsmith, Holly Krambeck, Charles Wang, Griya Ruffianne, Sebastian Anapolsky

